Many of us know we need to rethink economics, but Kate Raworth actually did it. Envisioning the economy as a doughnut, two boundaries become clear. If we fall into the doughnut’s middle hole, human needs fail to be met. If we drop off of the outer edge, life is unsustainable.
You should be weary of people who seek to get the “first lick” on a young impressionable brain. Paul Samuelson knew that by writing a successful economics textbook, he could influence how students frame the economy, and thus the world. From the 50’s to the 70’s, his textbook was the most widely used in introductory economics courses. Today, that role has been given to Gregory Mankiw’s “Macroeconomics” (see the Open Syllabus Project). Both view the economy in the same narrow way, with the same simple pictures that don’t seem useful today. Raworth’s Doughnut Economics breaches the pattern and envisions a new economics, for a new generation with clearly defined challenges and scant tools to solve them.
For so many years, the principle goal of economics, and thus the economy, has been GDP growth. Growth for whom or through what means wasn’t nearly as important as just ensuring there was in fact growth. Raworth emphasizes the importance of framing, and if you ask an economist what picture they foresee for GDP, they often describe an upward exponential function.
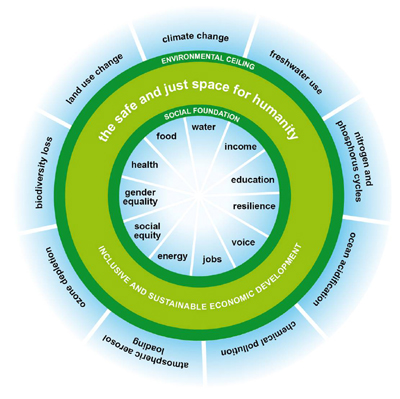
Thankfully, many young students that I’ve met recognize that infinite growth is unsustainable. Hopefully, their generation can popularize a GDP graph in the shape of a sideways S, respecting the upper bound to growth we have to live within. Enter Raworth’s doughnut. In Raworth’s framework, the outside of the doughnut reflects an upper bound we can not pass based on environmental limits of our planet. The inside of the doughnut reflects a social foundation we can not let crack, the necessities for humanity to thrive.
The goal should no longer be growth, but ensuring we take care of our social foundation and respecting our environmental ceiling. Raworth calls this balanced space in the middle the safe and just space for humanity, and that’s the goal we should direct ourselves toward. We can not ignore who growth is leaving behind, or what damage this growth is doing to our planet. These bounds are the crucial factor for Kate’s “doughnut.” They can move us beyond a narrow single measure called GDP, to looking at all the interconnected measures that are so important for our livelihood.
Once we’ve moved beyond the single measure, we have to also abandon the single neoclassical narrative that espouses the godlike nature of “the market”. The market, the household, the state, and the commons all have a place in the big picture, and different challenges have to be faced by different actors. The neoclassical story tells us there is a “tragedy of the commons,” what if that story was actually the tragic one? Kate takes a stab at the characters of the old narrative, and offers us a new script for them.
EARTH, which is life-giving—so respect its boundaries
SOCIETY, which is foundational—so nurture its connections
THE ECONOMY, which is diverse—so support all of its systems
THE HOUSEHOLD, which is core—so value its contribution
THE MARKET, which is powerful—so embed it wisely
THE COMMONS, which are creative—so unleash their potential
THE STATE, which is essential—so make it accountable
FINANCE, which is in service—so make it serve society
BUSINESS, which is innovative—so give it purpose
TRADE, which is double-edged—so make it fair
POWER, which is pervasive—so check its abuse
The big picture story requires the next generation of economists to be savvy with systems thinking. The old economics used mechanical equilibrium thinking, where economies trend towards a static state. A new economics recognizes the flaws of this equilibrium thinking, recognizing like Minsky said that “stability is destabilizing.” A new framework for economics will recognize the different feedback loops that influence the economies stability.
The language of complexity, evolution and systems needs to infiltrate economics. We need to be thinking about how we can design a resilient economy, one that can resist shocks. We need to look at the big picture, understanding the sources and sinks of different resources. We have to know where our food comes from, ensuring it is distributed properly, and we have to know where our plastic is being disposed, ensuring it’s not destroying the planet. We have to get familiar with the language of stocks and flows, the stores of resources and also their movements. These will be our new tools.
Raworth’s story gives hope to the young economists that are bent on saving the dying planet we’ve inherited. Her vision for a new economics, and the new economy, align with the work we’ve been doing here at The Minskys. Even better though, she has produced a frame for which we can better espouse our ideas. We started out thinking about systems – the sources and sinks of money creation. We’ve recognized the physics envy of mainstream economics. We understand the need to nurture human nature, so maybe we should be studying the grants in the economy and not just monetary exchanges. Without this, we’ll fall inside the doughnut’s hole, where there is no paid maternity leave, and austerity all around. We’ve also thought about ways not to breach the doughnut’s bounds, with a Green Job Guarantee, Basic Income, or Community Currencies for example.
Raworth’s doughnut frames the important aspects of the economy, and is simple to use. Observe your local community! Do you see human needs not being nurtured? That means we’ve breached the inside of the doughnut. Do you see irresponsible damage being done to our home, the earth? Then we’ve breached the outside of the doughnut. We have to design solutions to keep us in the doughnut. We’re all economists now, because we have to be. The future is pretty bleak for humanity without a planet to stand on.
If you too wish to start thinking like a 21st century economist, be sure to check out the book in it’s entirety here. There are also a series of animated shorts here. After that, it’s as simple as grabbing a pencil and drawing a doughnut.